
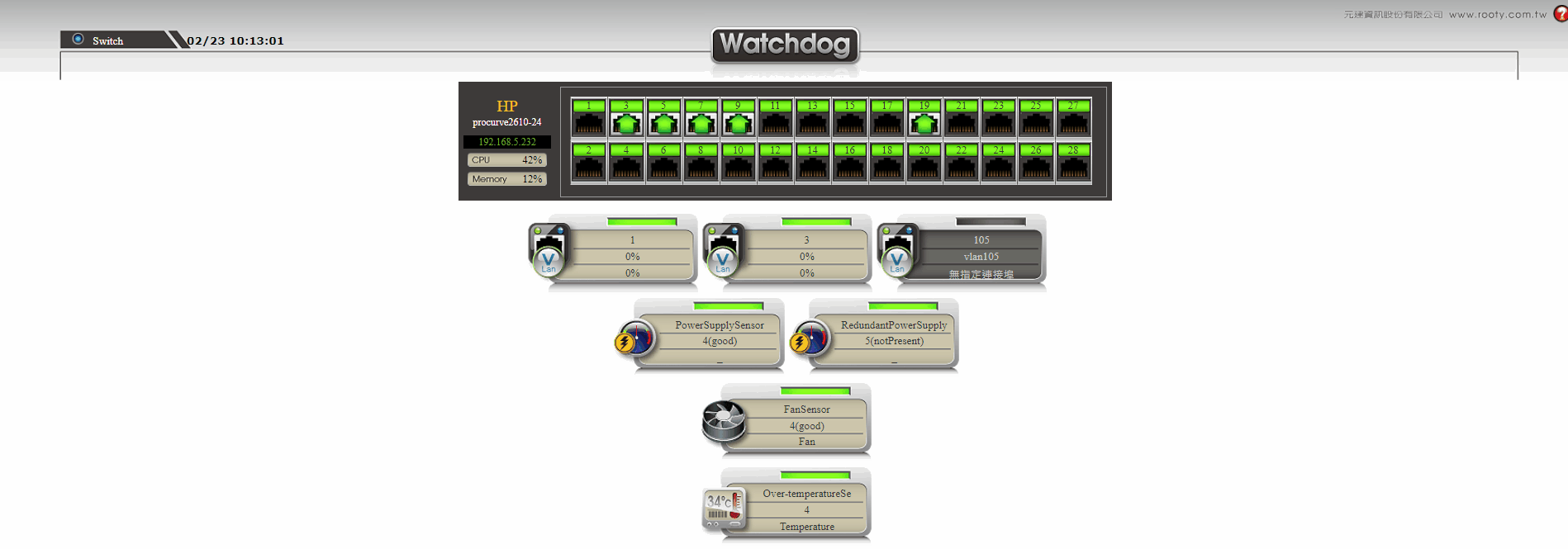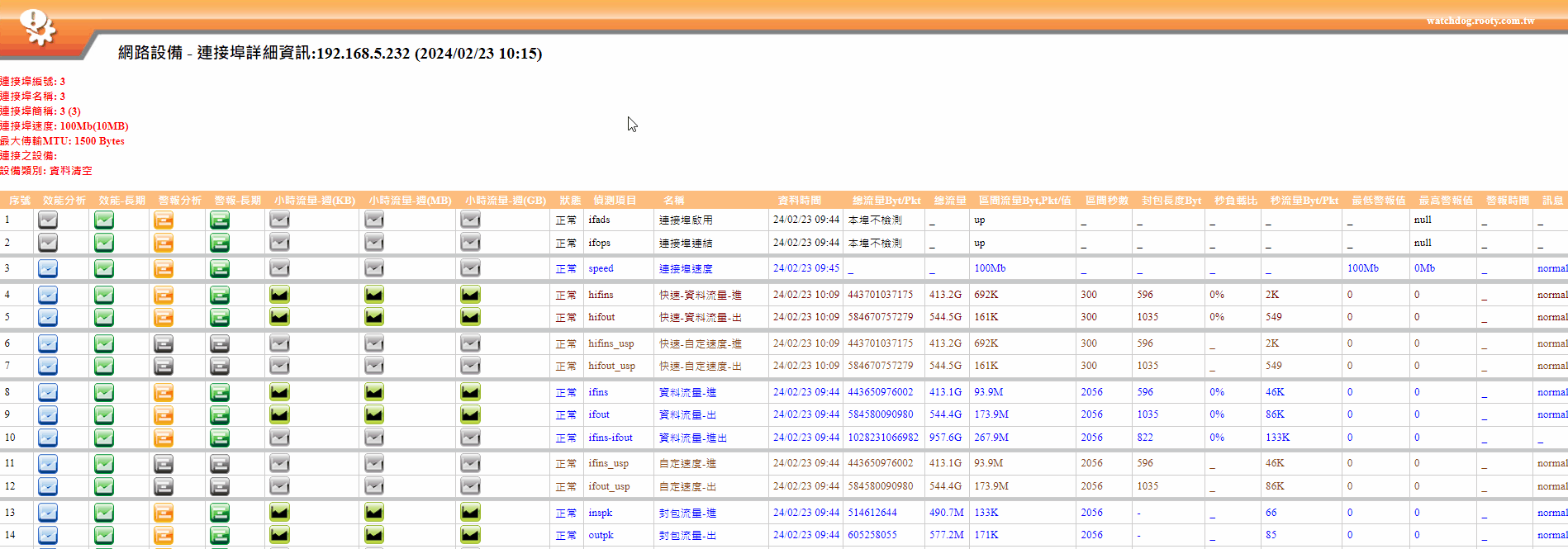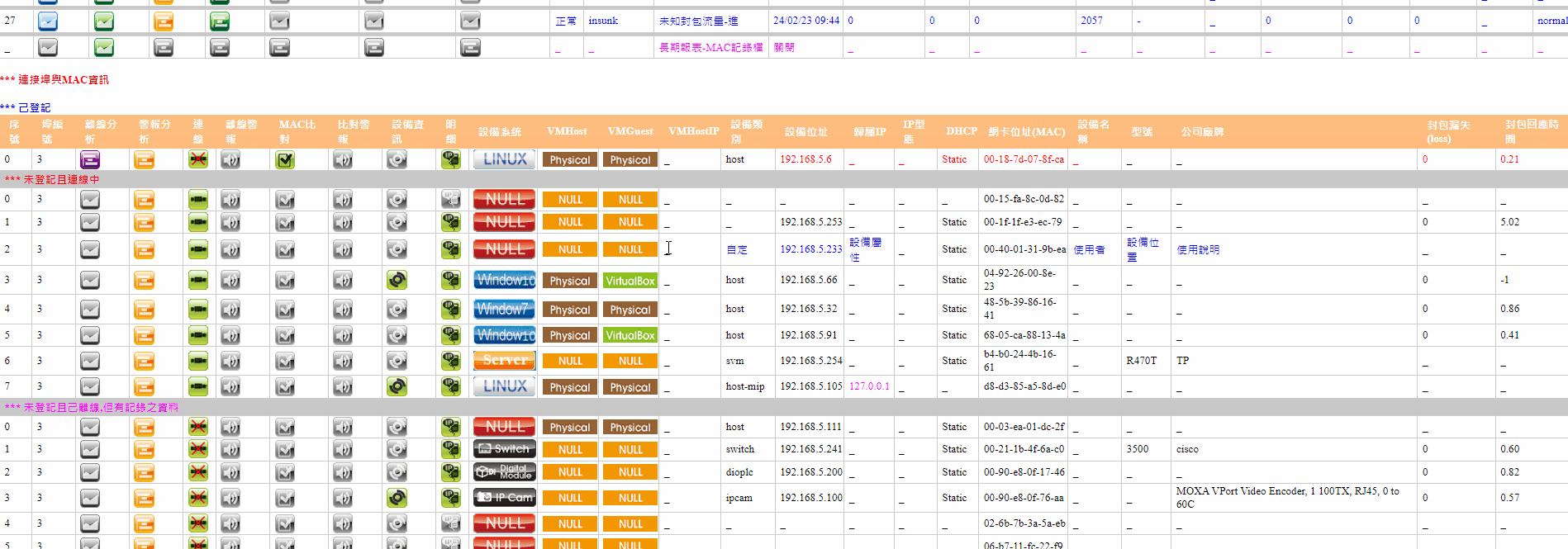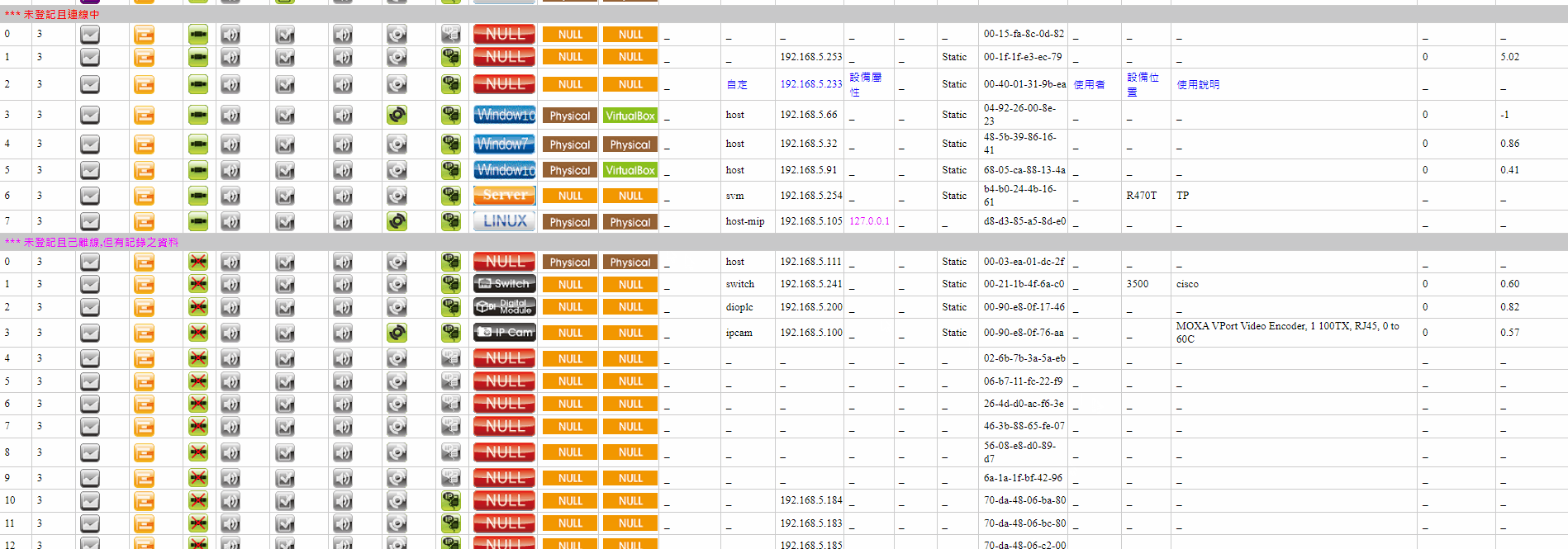
With the advancement of technology and the growth of business demands, choosing a suitable operations monitoring system has become increasingly important.
This is not just about monitoring the operational status of hardware devices or software applications but a comprehensive strategy involving real-time data analysis, security assurance, and business continuity maintenance.
Therefore, when enterprises choose an IT operations monitoring system, they must consider a range of conditions and capabilities to ensure that the system not only meets current needs but can also flexibly respond to future challenges.
The following are the conditions to consider when choosing an IT operations monitoring system:
➣The ability to control and monitor the types of equipment in the information room (the more, the better the integration).
➣Whether the monitored equipment and its items can comprehensively penetrate various functional structures of the information equipment.
➣The methods of obtaining information data, depth, and analysis capabilities, and the mechanisms of system simulation testing.
➣Detailed information on servers of different platform systems (hardware, operating system, application system, network connection, information security).
➣Detailed information on network equipment (e.g., tracking IP connections in and out of each switch port).
➣Real-time correlation information of various types (e.g., the relationship between the host and switch ports).
➣The ability to integrate various application systems and unify control methods.
➣Whether data retention and application can be divided into real-time information, short-term graphical analysis (7 days), and long-term data (one year or unlimited).
➣The rigor of the alert detection mechanism and the diversity of alarm notifications.
➣The self-monitoring ability of the operations system, including platform resources and performance, system program survival, and alarm equipment detection.
➣Emergency response (e.g., emergency shutdown during power outages).
➣The ability of the real-time information - war room.
➣The familiarity of the agent or manufacturer with the application of the monitoring system.
➣Customization capabilities and local maintenance culture.
➣The difficulty for IT personnel to establish and learn the operations monitoring system.
➣Conformance to localized organizational structure and system personnel characteristics.
Additionally, our company's self-created F0 to F5 grading system provides a framework for enterprises to evaluate the operations monitoring system.
This grading system, from F0 level (basic level) to F5 level (highest level), gradually increases the requirements for the functions, integration capabilities, automation degree, and anomaly handling capabilities of the operations system.
Each level represents different stages of the operations system in terms of technical maturity, monitoring depth, alert mechanism, user interface friendliness, and customization capabilities.
➣F0 level: Represents the most basic manual detection method, relying on system personnel to actively or regularly detect, lacking automation and alert notifications.
➣F1 to F4 levels: Gradually introducing automated tools and detection software, improving the efficiency and accuracy of anomaly detection, but varying in integration capabilities, automation degree, and alert notifications at different levels.
Click here to view the detailed 【F0-F5 Grading Table】
F5 Level — Built to the Highest Standards
The F5 level represents our company's highest standard for IT operations monitoring systems,
designed to meet the complex and diverse information technology environments.
This level emphasizes comprehensive monitoring of various information devices, whether servers, network equipment, or storage systems.
The F5 level system can obtain information or execute commands through the most suitable methods to achieve broad support for all devices and brands within the entire IT information room.
The core feature of the F5 level lies in its integrated design concept, enabling it to support multiple server operating systems,
including but not limited to Windows series, Linux series, IBM AIX, HP-UX, SUN Solaris, SCO UNIX, and FreeBSD.
Additionally, by installing specially designed agent programs on the servers, the F5 level system can provide more complete and in-depth monitoring functions,
allowing IT managers to effectively monitor, analyze, and manage IT infrastructure.
The WATCHDOG system is developed based on the high standards of the F5 level, aiming to provide enterprises with a comprehensive and efficient IT operations monitoring solution.
Combining advanced technology with extensive industry experience, the WATCHDOG system not only achieves comprehensive monitoring of various operating systems and devices
but also provides customized monitoring strategies and response plans based on the characteristics of different devices and environments.
Through the practical application of the WATCHDOG system, enterprises can effectively enhance the stability and security of their IT infrastructure, while also improving the efficiency and flexibility of information management.
The overall design architecture is as follows:
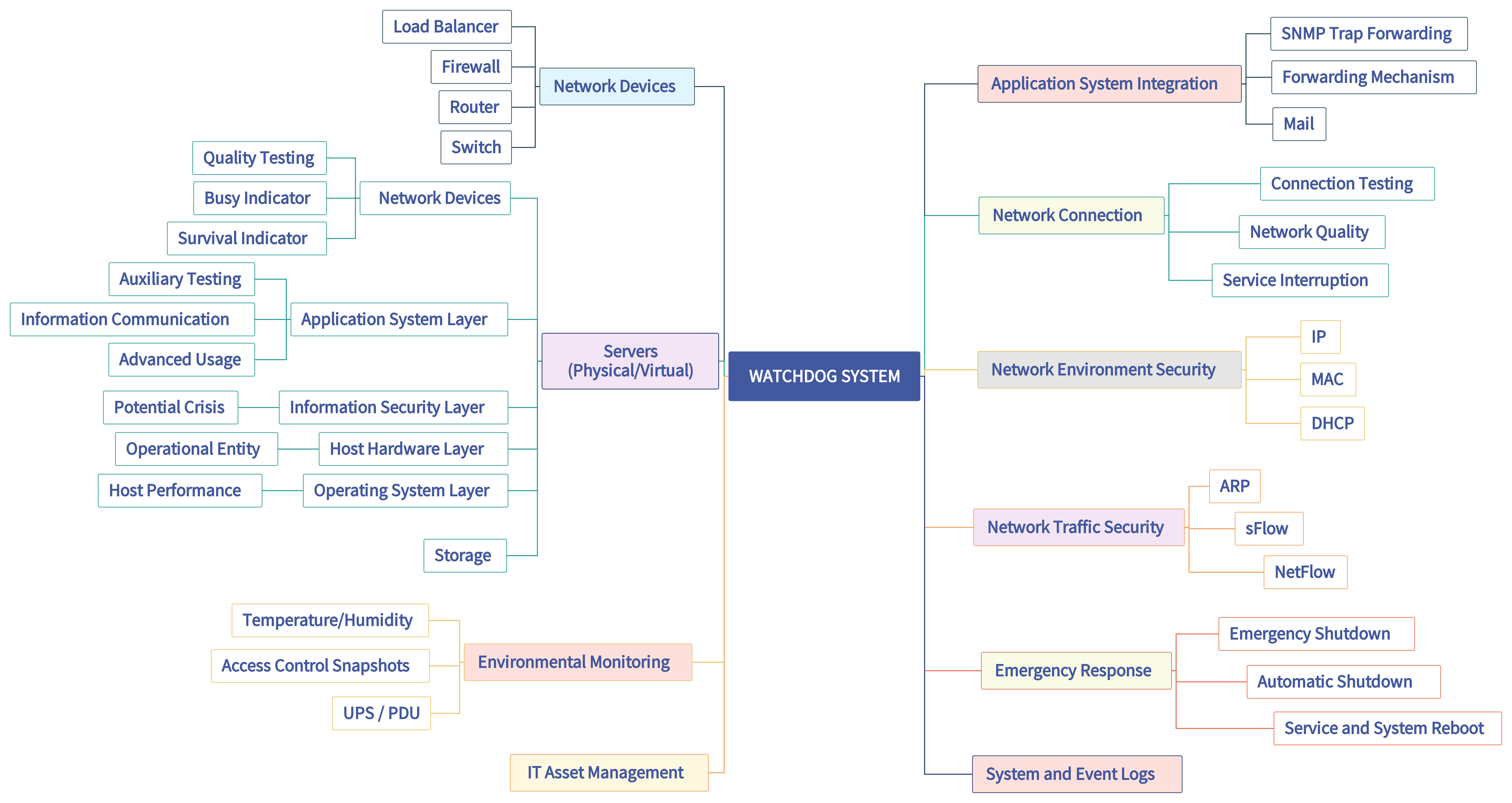
Through IPMI, ILO, IMM, iDRAC, and other management protocols, the WATCHDOG system can conduct in-depth monitoring of the hardware status of the server host,
covering power supplies, temperature sensors, fan speeds, and voltage and current safety indicator data to ensure the reliability and stability of server operations.
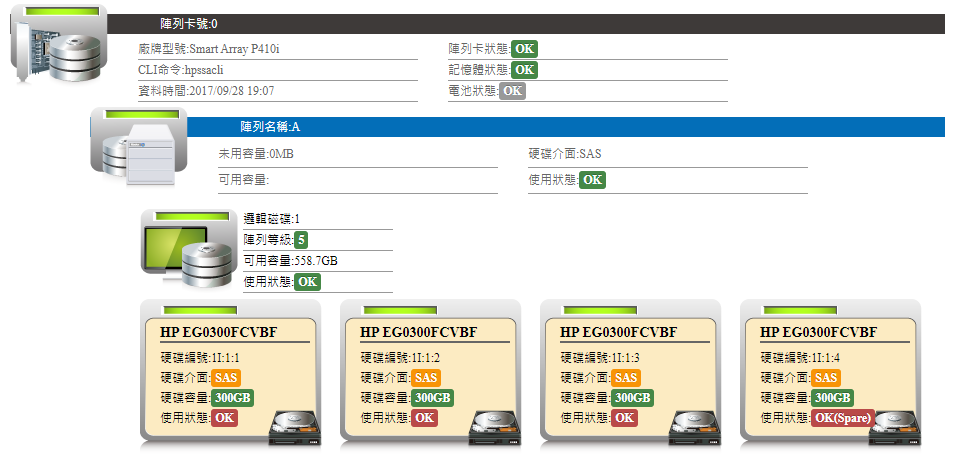
In terms of RAID monitoring, the WATCHDOG system supports common RAID brands such as HP Smart Array, Adaptec RAID, and LSI MegaRAID,
enabling monitoring of RAID cards, array disk groups, logical disk groups, and physical drives, as well as detecting the addition and removal of devices and monitoring the hardware and organizational status of the devices.
It provides detailed monitoring of the usage status information of logical disk groups and physical drives, including but not limited to the following abnormal messages:
➣Failed or removed physical drive
➣Rebuilding, showing progress percentage
➣Ready for rebuild
➣Failed physical drive
➣Data drive in use
➣Spare drive
➣Unassigned drive
➣Rebuilding disk
By installing a specialized agent program, the WATCHDOG system provides more complete and accurate hardware layer monitoring,
ensuring optimal performance and data security of the server host under various conditions.
These features ensure that the WATCHDOG system can identify hardware abnormalities in real time and take appropriate measures promptly.
The WATCHDOG system's operating system layer monitoring functions are designed to capture and analyze key performance indicators of the operating system.
This layer of monitoring ensures the health of the operating system, thereby supporting the stable operation of the entire IT environment.
Key Operating System Information:
➣System location, operating platform, and platform version
➣Host name, network settings
➣Program status and version
➣Network card information, connection status
➣Currently running programs, scheduled tasks, DLL programs
➣Processes, network status (TCP, UDP, ARP)
➣Security identifiers
WEB Command Line:
➣Create common command combinations or scripts through the browser
➣Obtain usage instructions for various operating system commands
➣System resource usage status:
➣CPU Usage
➣Physical memory and virtual memory usage
➣Disk (Filesystem) usage
➣Filesystem inode usage (for Linux/Unix)
➣Disk performance (read/write I/O performance)
Program and Service Monitoring:
➣Running programs (detecting and counting the number of programs that should be running or LISTEN services)
➣Resident programs (Linux/Unix)
➣System services (Windows)

The network connection layer monitoring function focuses on evaluating the health status and performance of the enterprise network connections.
This layer's function is crucial to ensuring that information flows smoothly and unobstructed within the network.
The following are the key monitoring functions provided by the WATCHDOG system at the network connection layer:
➣Agent detection - Packet test: Monitor packet transmission status of devices not in the local segment.
➣Agent detection - IP ports: Detect IP port opening status of devices not in the local segment.
➣Agent detection - Scheduled files: Monitor scheduled files of devices not in the local segment to ensure consistency and reliability of file transfers.
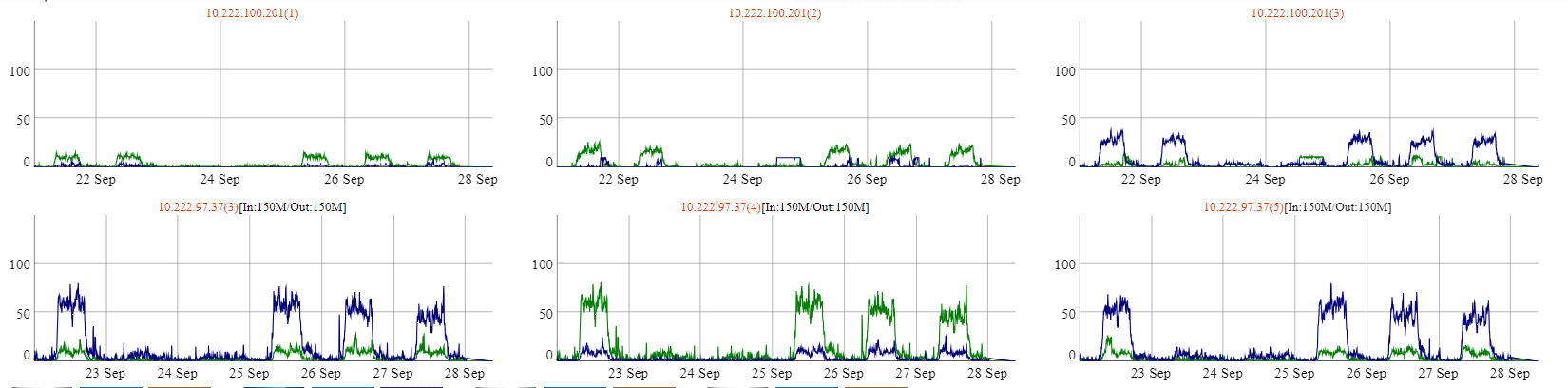
➣Network card traffic monitoring: Real-time monitoring of network card traffic per second, promptly detecting and preventing network congestion.
➣Connection count statistics: Count the number of current connections based on IP address and port to evaluate network load.
➣Connection speed test - Receive/Send: Test the actual output performance of the network through simulating data transfer speeds.
This layer of monitoring ensures that the enterprise's critical application systems can run smoothly and respond quickly when problems occur.
The following are the key monitoring functions provided by the WATCHDOG system at the application system layer:
➣Execution program monitoring: Monitor and count the number of programs that should be running to ensure that necessary services and applications run at the correct time.
➣File count statistics: Calculate the number of files in a specific directory or folder to monitor data storage conditions.
➣File detection: Track file modification times and capacity changes to stay alert to data changes within the system.
➣Event alarms: Integrate with application systems to issue real-time alerts for abnormal events, quickly responding to potential issues.
➣Event data analysis: Assist application systems in analyzing data-type events and issue alerts when anomalies are detected.
➣Scheduled information monitoring: Monitor the scheduled execution tasks of applications, analyze the progress of tasks, and issue alerts for anomalies.
This layer focuses on preventing unauthorized access and detecting potential security vulnerabilities within the system. Implementing effective security monitoring measures helps detect and prevent security threats early.
The following are the key monitoring functions provided by the WATCHDOG system at the information security layer:
➣External network connection test: Test possible connection points to external networks to ensure no improper external access.
➣Illegal TCP LISTEN detection: Detect and identify unauthorized TCP LISTEN activities to prevent potential intrusions.
➣Illegal program execution detection: Identify and report any unauthorized executed programs.
➣Illegal disk mounting detection: Detect any unauthorized disk mounting behavior within the system.
➣Illegal network card mounting detection: Ensure the use of network interface cards is legitimate and secure.
➣Program tampering comparison detection: Detect any unauthorized program modifications through 100% binary comparison.
➣File and directory tampering detection: Monitor folder contents to ensure files and programs have not been tampered with.
➣System program tampering detection: Detect any abnormal changes in system program files.
➣Operating system package comparison: Compare the entire operating system package to detect illegal changes.
➣Running program tampering comparison: Real-time monitoring of running programs to ensure they have not been tampered with.
➣Illegal file detection: Search and report any illegal files in the root directory.
➣System new file or program monitoring: Track new files or programs added to the system to prevent malware intrusion.
These meticulous security detection features make the WATCHDOG system a solid security shield for enterprise information.
Through comprehensive monitoring and real-time response mechanisms, it helps enterprises timely detect and respond to various security threats, maintaining business continuity and data integrity.
The WATCHDOG system's monitoring capabilities for virtual hosts cover comprehensive monitoring from the hardware layer to system resource allocation, ensuring the efficient operation and security of the virtualized environment.
Virtual host (VM) technology has become an indispensable part of modern IT architecture.
The following are the key features provided by the WATCHDOG system in virtual host monitoring:
Virtual Host - Hardware Layer
Obtain security indicator data status such as power supplies, temperature sensors, fan speeds, and voltage and current through IPMI, ILO, IMM, iDRAC, and other protocols.
Virtual Host - Operating System Layer
➣CPU usage: Monitor CPU load.
➣Memory usage: Track the usage of physical and virtual memory.
➣Disk (Filesystem) usage: Monitor the usage status of disk space.
➣Key operating system information: Provide over 200 system information items, including hardware list, iSCSI list, network interfaces, and software configuration.
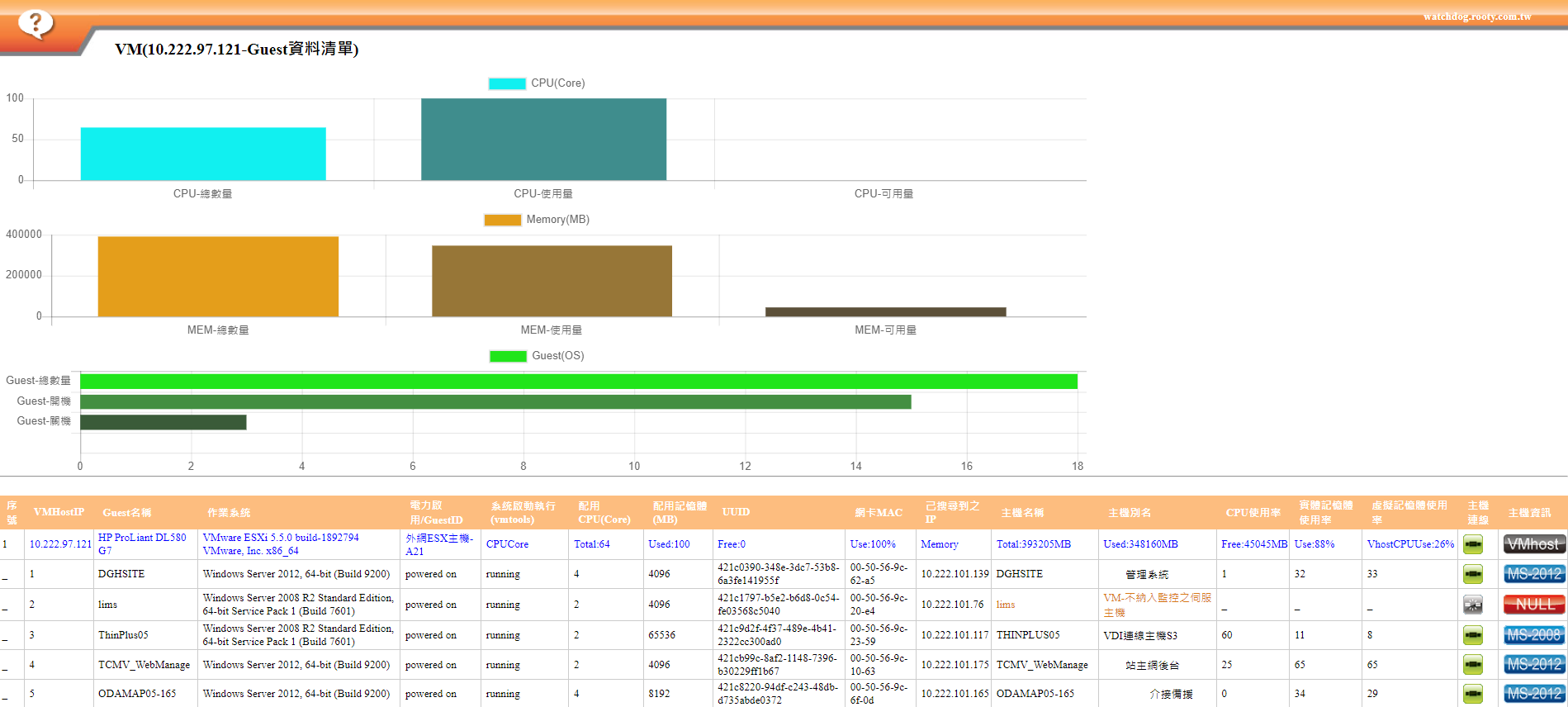
Virtual Host - VM System Resources
➣Provide detailed virtual host system resource and guest host resource allocation charts,
including VMHost CPU Core, Memory, host brand, and the number of guest hosts.
➣Record the resource allocation status of guest hosts, such as CPU Core, Memory, VMTools installation status, and PowerOn/Off status.
Virtual Host - RAID
➣Brand support: Compatible with common RAID brands, including HP Smart Array, Adaptec RAID, and LSI MegaRAID, ensuring broad application scenarios and hardware devices.
➣New device detection:
RAID card: Monitor newly added RAID cards.
Array disk group and logical disk group: Track newly established arrays and logical partitions.
Physical drives: Detect newly added physical drives.
➣Device removal detection: Similar to new device monitoring but for removal operations.
➣Device hardware status monitoring:
RAID card and memory status: Ensure RAID card and its memory are functioning normally.
Battery status: Monitor the health of the RAID card battery, which is crucial for protecting cached data.
➣Device organizational status detection:
Detailed record and monitoring of the operational status of various components in the RAID, including but not limited to:
Logical disk group and physical drive usage status: Covering various states from normal operation to rebuilding, such as indicating a failed drive and rebuild progress.
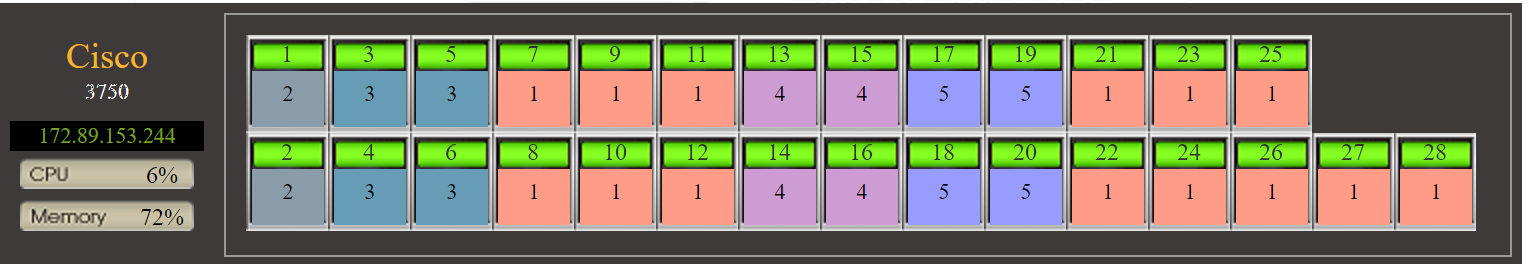
This module focuses on monitoring key network devices such as switches (L2, L3 Switch), routers (Router), firewalls (Firewall), UTM, and load balancers (Load Balance) to ensure network continuity and security.
The following is an overview of the WATCHDOG system's network equipment monitoring functions:
Hardware Layer
➣CPU usage ratio
➣Memory usage ratio
➣Power supplies, temperature sensors, fan status
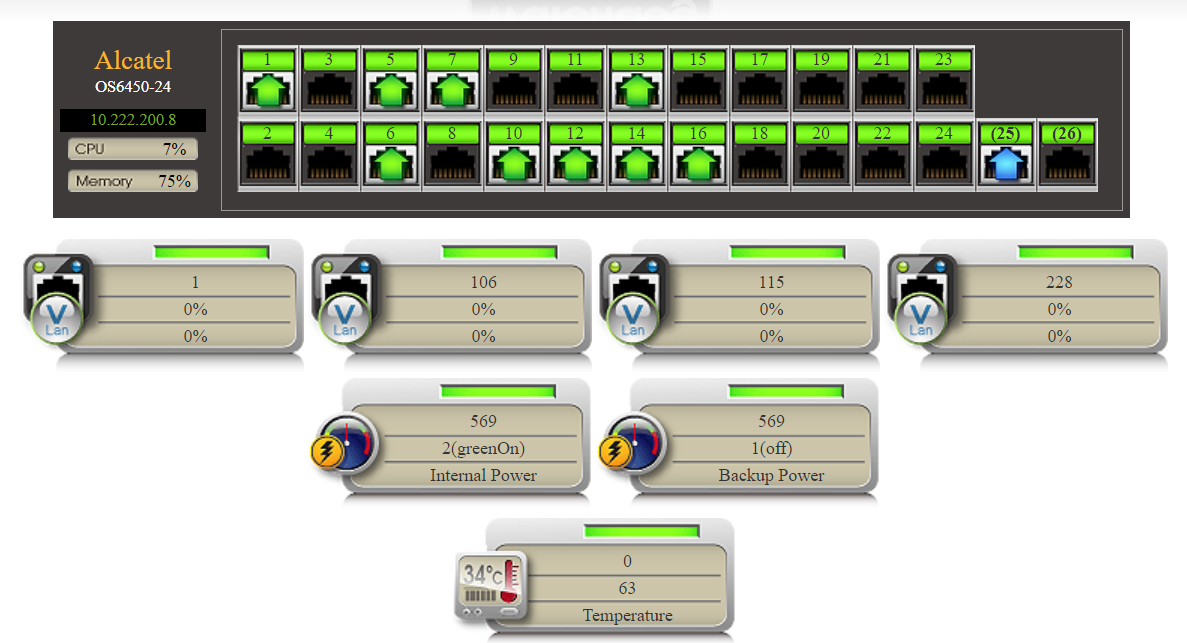
Interconnection Structure
➣Interconnection topology map: Display the association between each connection port (PORT) and MAC, IP, device information (e.g., server).
➣Information equipment location map
➣Traffic analysis and records: Including traffic ratio/second, Bytes, packet statistics, port speed, MTU, and analysis, statistics, and information by the entire SWITCH, VLAN, and each port.
For example: Packet traffic ratio - in/out,
Packet traffic number - in/out,
Broadcast packet traffic - in/out,
Error packet traffic - in/out,
Ignored packet traffic - in/out,
Unknown packet traffic - in/out,
Status Information
➣VLAN distribution map
➣Port speed distribution map
➣Various packet traffic ranking charts
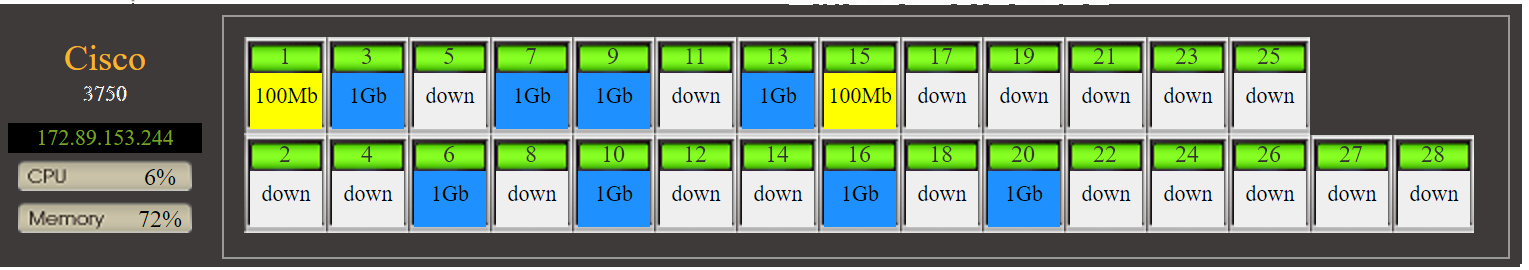
Advanced Features
➣Search switch port location by IP: Enter an IP to directly search for the switch's location and port.
➣Track source and destination IP switch ports: Enter the source IP and destination IP to display the association diagram of the switch locations and ports between the two IPs.
➣Customizable port speed: Customizable port carrying speed to calculate accurate traffic ratios for leased lines (e.g., GSN).
➣WEB CLI (Command Line Interface): Obtain switch settings and status information at any time through predefined CLI commands.
➣Configuration file backup: Automatically back up configuration files regularly, compare differences with the previous backup, and issue alarm messages.
➣Graphical display: Display as close to the actual panel design of the switch as possible, especially the module arrangement of core switches.
Alarm Items
Alarm mechanisms based on the entire SWITCH, VLAN, and each port, including switch hardware layer, various traffic numbers, port enable/disable (down/up), port speed, MAC control, offline alarms, etc.
The WATCHDOG system provides a range of functions to track and analyze network traffic, ensuring network security and performance in terms of network traffic and security monitoring. By deeply analyzing traffic data such as NetFlow and sFlow, the system can identify different types of network activities, helping managers take appropriate measures against potential security threats and performance bottlenecks.
The following is an overview of network traffic and security monitoring functions:
Network Traffic Monitoring:
➣Supports NetFlow and sFlow protocols, capable of analyzing traffic of TCP, UDP, ICMP, IGMP, ARP-Request, and ARP-Reply protocols.
➣Can display destination IP, destination port, source IP, and source port.
➣Provides country domain, external IP country attribution, dangerous IP, and general protocol IP analysis.
➣Statistics and classification of IP quantity, times, Bytes, packets, providing analysis charts and detailed information for different categories.
➣Country domain and IP distribution map, built-in global domain and IP database.
Alarm Items:
➣Define internal and external network traffic.
➣Define outbound and inbound traffic.
➣Alarms based on destination IP and destination IP plus port.
➣Hourly total traffic (in MB and packets).
➣Hourly total number of times.
Network Traffic - ARP Monitoring
➣Collect and analyze ARP-Request and ARP-Reply traffic, and statistics on the total number of times per hour for source IP.
➣Reduce the risk of IP conflicts, control illegal private access devices, and ensure correct pairing and management of IP, MAC, and DHCP servers.
The WATCHDOG system provides comprehensive detection and analysis in network connection monitoring to ensure the effective monitoring of network communication quality and device connection status.
Through a series of tests and detections, the WATCHDOG system can detect network issues in real-time, helping to maintain the stable operation of the network and the availability of services.
The following is an overview of network connection functions:
Packet Test:
Regularly execute ping operations to monitor the loss rate and response time of ICMP packets, assessing network quality and device connection status.
IP Ports:
Regularly check the LISTEN ports of network service programs to ensure the normal operation of services.
Domain Detection:
Test the response time of domain name resolution (IP) to specified DNS servers to assess network quality.
Website Detection:
Regularly detect website operation status, including DNS resolution, connection status, middleware and backend database connections, web page retrieval time, web page content, service systems (e.g., Apache, IIS, GSE), and web page retrieval status codes (e.g., 200, 404, 505).
Connection Speed Test - Send and Receive:
Measure the transmission speed and quality of computers over the network to understand the possible locations and causes of network speed issues in-depth. For example, measuring the network transmission speed from computer A to computer B (e.g., transferring 20MB of data at 100MB/s).
Through these comprehensive monitoring functions of the WATCHDOG system, enterprises can monitor and evaluate the performance of their network connections in real-time, quickly identifying and resolving potential network issues, ensuring stable network operation and efficient business operations.
The WATCHDOG system's application system integration mainly uses the following four specialized functions to seamlessly integrate other applications into the WATCHDOG system, thereby building an efficient alarm system:
Scheduled File:
This function requires the specified application to regularly report a 【password】,
and the WATCHDOG system confirms the survival status of the relevant application or service by receiving and comparing this 【password】.
Alarm Gateway:
Provides an interface that allows project applications to directly send alarm or alarm clearance data to the WATCHDOG system. When the application detects a situation that needs immediate attention, it can quickly send the alarm information to the monitoring center through this gateway.
Event Data:
Specifically designed for applications that need to monitor specific data indicators. The WATCHDOG system can read a file containing numbers and determine whether to issue an alarm based on this number. This allows data-sensitive applications to trigger alarms when reaching specific thresholds.
Information Collection:
The WATCHDOG system can collect and analyze information from various system logs (such as system logs of Unix/Linux/Switch or event logs of Microsoft Windows). This not only helps to standardize log data but also issue alarms based on the level classification or specific message content in the logs, responding to potential problems in a timely manner.
Through the integration of these functions, the WATCHDOG system provides enterprises with a powerful monitoring and alarm platform, allowing application developers and IT administrators to monitor the operational status of application systems more effectively and respond to problems in a timely manner.
The forwarding mechanism of the WATCHDOG system is designed to effectively manage and quickly respond to various alert messages.
Through simple network management - SNMP TRAP and email forwarding functions, the WATCHDOG system can integrate and forward alerts from different devices, ensuring the stability and security of the enterprise IT environment.
Simple Network Management - SNMP TRAP:
This function allows the WATCHDOG system to receive SNMP TRAP messages from other information devices, which may be issued due to equipment failures or specific events.
It can effectively integrate alert messages from storage systems, network equipment, etc., such as hard disk failures, network connection abnormalities, etc., for unified management and processing.
Email Forwarding - Local Mailbox and Remote Mailbox:
Through the email forwarding function, the WATCHDOG system forwards alert messages to designated local or remote mailboxes, enhancing the visibility and response speed of alerts.
Suitable for alert events issued by firewall, UTM, access control systems, environmental control systems, etc., ensuring relevant personnel can obtain alert information promptly and take necessary measures.
Integrate other equipment environmental control systems, access control systems, and add missing monitoring equipment
(e.g., temperature collectors, humidity collectors, personnel movement photography in the data center)
Integrate cabinet PDU power systems with emergency shutdown of various information equipment, etc.
The emergency response function in the WATCHDOG system is designed to provide quick and effective responses to different emergency situations. Through carefully designed emergency execution commands for the characteristics of the operating system,
WATCHDOG can activate preset standard operating procedures (SOPs) in case of power outages, flooding, fire alarms, earthquakes, or network attacks. The core elements of the emergency response function are as follows:
Emergency execution commands: Combine a series of emergency execution commands based on the different characteristics of the operating system to respond to sudden events.
Establish standard operating procedures (SOPs):
➣Power outage: Develop emergency response measures for power outages to ensure the safety of critical equipment and data integrity.
➣Flooding: Activate preset evacuation and equipment protection procedures when the data center faces a risk of flooding.
➣Fire alarm: Develop emergency evacuation and equipment protection measures in case of fire, ensuring personnel safety and minimizing property loss.
➣Earthquake: Follow SOPs to respond quickly during an earthquake, reducing damage to equipment and ensuring personnel safety.
➣Network attack: Quickly activate network defense and data protection measures in case of network attacks to prevent data leakage or system damage.
Emergency shutdown procedure:
When necessary, the WATCHDOG system can execute an emergency shutdown procedure, quickly shutting down the system safely to protect the system and data from further damage.
In IT operations monitoring systems, efficiency of monitoring items, integration associations, alert efficiency, detection items, and understanding and managing long-term and short-term data collection and related information are crucial.
The following is a detailed list of these core concepts to provide a clear perspective on how we classify the operations system:
Efficiency of Detection Items
The detection items for each device reach 100 points. If there are 100 devices, the number of detections per hour is 12 times, equivalent to 120,000 detections per hour, reaching 2,880,000 detections per day.
Integration Associations
➣Local resource associations: such as CPU performance and motherboard temperature, fan speed, and process associations with CPU, memory, disk, I/O performance.
➣Network connection associations: such as the association between server network performance and switch, network cabling panel quality, and network traffic.
➣Dependency associations: such as the association between servers and UPS.
Alert Efficiency
➣Alert efficiency depends on the characteristics and importance of information equipment, requiring different bases.
➣Includes the ability to calculate and count related events, and the ability to calculate with other information items after obtaining information.
➣The rigor of alerts and sensitivity of alarms is determined by the product of the number of detections and the interval time.
Detection Items
Defined based on information equipment, including facilities, performance, resources, and records.
Long-term and Short-term Data Collection
Used to compare whether the equipment system is in a long-term state or a short-term phenomenon, such as the CPU usage rate remaining at 80% for a long time, which may indicate normal operation status.
Related Information
Analyze the problem of slow connection speed perceived by users, which may involve multiple aspects, including user computers, network connection lines, network cabling panels, switch settings or connection lines, servers, etc.