
Network Traffic - ARP Main Function
ARP (Address Resolution Protocol) is a protocol used to map a network layer address (like an IP address) to a data link layer address (like an Ethernet address).
It is a critical step that allows data to be sent from one host to another.
The process involves two main steps: ARP Request and ARP Reply.
➢ ARP Request:
When a host needs to send data to another host but only knows the target host's IP address and not its MAC address,
it sends an ARP Request. This request includes the sending host's IP and MAC address, and the target host's IP address.
This request is broadcasted to all hosts on the same network.
➢ ARP Reply:
When a host receives an ARP Request and the target IP address matches its own IP address,
it sends an ARP Reply. This reply includes the host's IP address and MAC address and is sent to the host that sent the ARP Request.
Through this process, a host can resolve the target host's MAC address and then correctly send data to the target host.
When a host (in this case, the WATCHDOG host) needs to send data to another host, it undergoes the ARP Request and Reply process.
WATCHDOG is responsible for collecting ARP information from the network.
WATCHDOG has a dedicated program to handle these collected ARP data.
The client does not need to specifically set or collect ARP information.
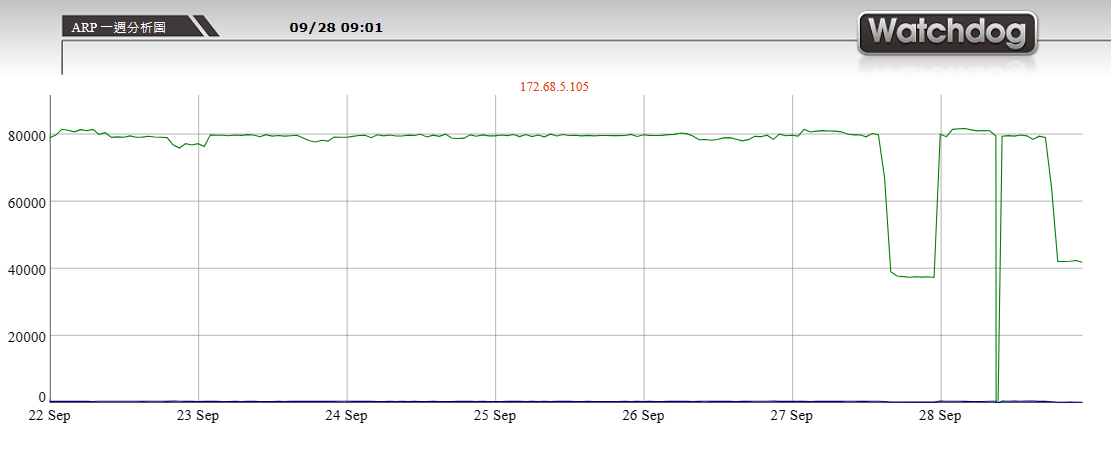
Applications of ARP
Since the ARP Request and Reply process involves data transmission across the network,
if there are too many ARP Requests or Replies in the network, it may cause network congestion.
Through analyzing ARP Requests and Replies, the cause of network congestion can be identified.
For example, we can identify which host or hosts are sending large numbers of ARP Requests and resolve the network congestion problem.
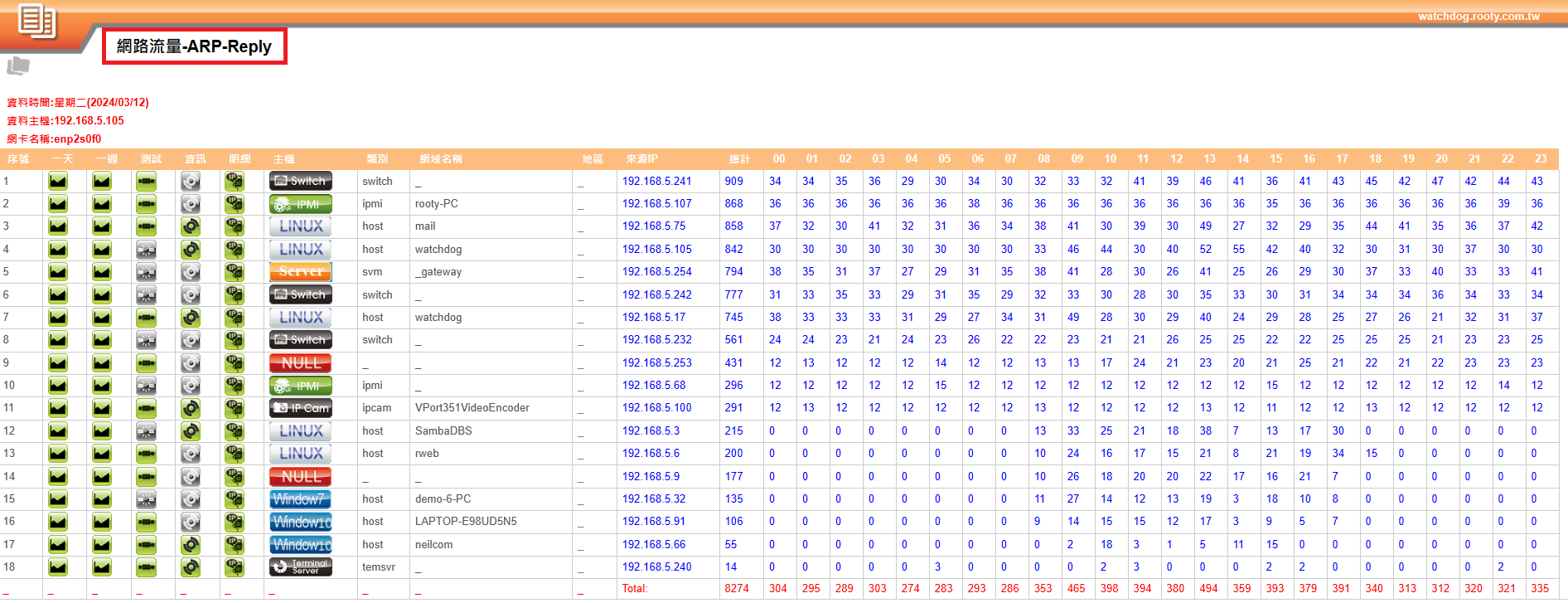
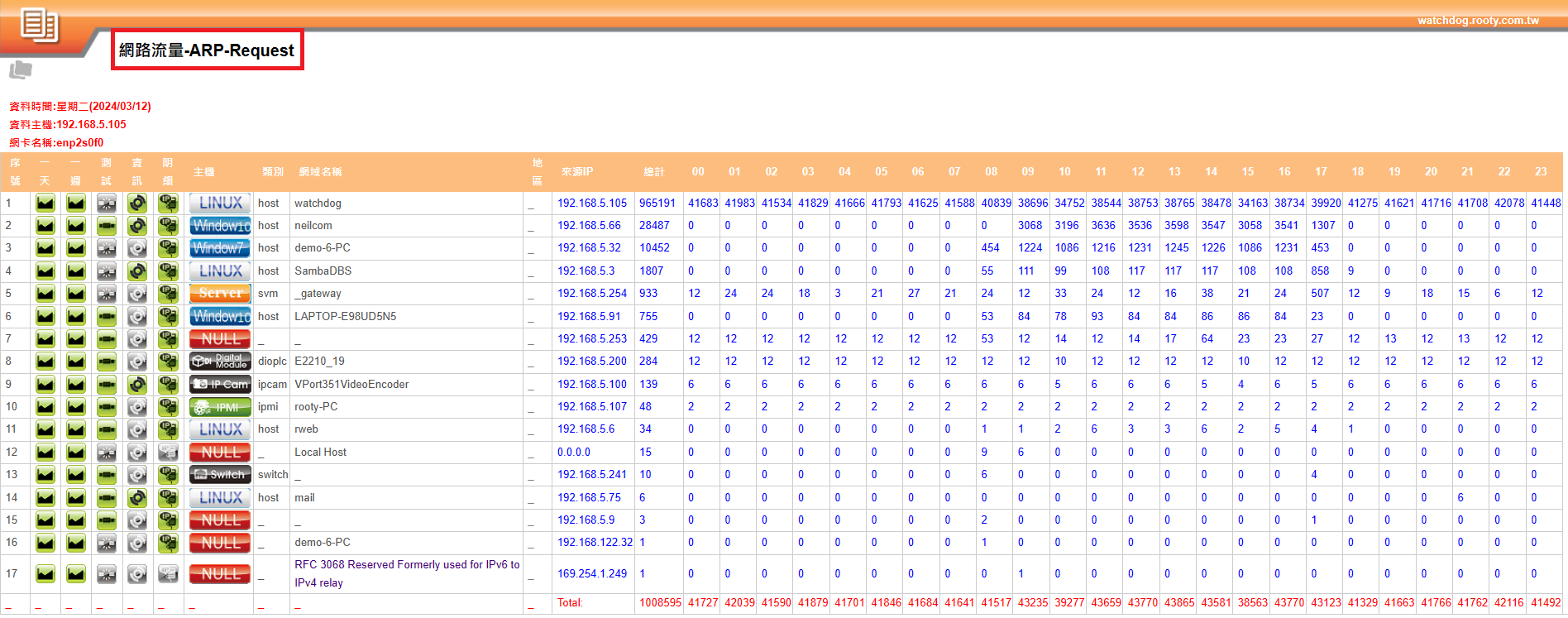
System Specifications for Monitoring ARP Requests and Replies
➢ Detection purpose: Real-time monitoring of ARP traffic within the internal network, allowing system personnel to understand if ARP traffic is normal.
➥Hourly request volume statistics
➥Hourly reply volume statistics
➥Daily total volume statistics
➢ Monitoring target: Monitor IP devices issuing ARP Requests and Replies within the internal network.
➢ Alarm conditions: Timely detection of abnormalities based on hourly statistics.
➢ Real-time information: Provide real-time data and alarm publication.
➢ Information collection: Record messages, data, and the publication and cancellation times of alarms.
➢ Emergency handling: Notify and execute predetermined programs in case of abnormalities.
➢ Alarm thresholds: Define alarm thresholds based on application needs.
To see the practical settings of [Network Traffic - ARP] on WATCHDOG, please explore further details through the [Network Traffic - ARP] link.